 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Bronica in Japan, Changnuo, Mai Xu Jia, Quan Kang Nuo in China and as Seradair in India. .[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablets, granules) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | >96% |
| Elimination half-life | 22 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.220.176 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
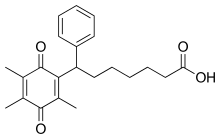
| Formula | C22H26O4 |
| Molar mass | 354.446 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Seratrodast (development name, AA-2414; marketed originally as Bronica)[2] is a thromboxane A2 (TXA2) receptor (TP receptor) antagonist used primarily in the treatment of asthma.[3][4] It was the first TP receptor antagonist that was developed as an anti-asthmatic drug and received marketing approval in Japan in 1997.[5] As of 2017 seratrodast was marketed as Bronica in Japan, and as Changnuo, Mai Xu Jia, Quan Kang Nuo in China.[1]
Unlike thromboxane synthase inhibitors such as ozagrel, seratrodast does not affect thrombus formation, time to occlusion and bleeding time.[6] Seratrodast has no effect on prothrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin time, thus ruling out any action on blood coagulation cascade.[7]
- ^ a b "Seratrodast international brands". Drugs.com. Retrieved 8 March 2017.
- ^ "Seratrodast". AdisInsight. Retrieved 8 March 2017.
- ^ Endo S, Akiyama K (November 1996). "[Thromboxane A2 receptor antagonist in asthma therapy]". Nihon Rinsho. Japanese Journal of Clinical Medicine (in Japanese). 54 (11): 3045–8. PMID 8950952.
- ^ Hada S, Hashizume M, Nishii S, Yoshioka F, Yasunaga K (January 1993). "[Study on the inhibitory effect of AA-2414 on platelet aggregation and its clinical effect in asthmatic patients]". Arerugi [Allergy] (in Japanese). 42 (1): 18–25. PMID 8457165.
- ^ Dogné JM, de Leval X, Benoit P, Delarge J, Masereel B (2002). "Thromboxane A2 inhibition: therapeutic potential in bronchial asthma". American Journal of Respiratory Medicine. 1 (1): 11–7. doi:10.1007/bf03257158. PMID 14720071. S2CID 40324562.
- ^ Dogné JM, Hanson J, de Leval X, Kolh P, Tchana-Sato V, de Leval L, et al. (May 2004). "Pharmacological characterization of N-tert-butyl-N'-[2-(4'-methylphenylamino)-5-nitrobenzenesulfonyl]urea (BM-573), a novel thromboxane A2 receptor antagonist and thromboxane synthase inhibitor in a rat model of arterial thrombosis and its effects on bleeding time". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 309 (2): 498–505. doi:10.1124/jpet.103.063610. PMID 14742735. S2CID 46723447.
- ^ Samara EE (1996). "Seratrodast (AA-2414)—A Novel Thromboxane-A2 Receptor Antagonist". Cardiovascular Drug Reviews. 14 (3): 272–85. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3466.1996.tb00231.x.