 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | (/sɛˈvɛləmər/ or /sɛˈvɛləmɪər/) |
| Trade names | Renagel, Renvela |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601248 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 0% |
| Excretion | Feces 100% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
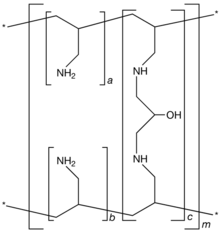
| Formula | [(C3H7N)a+b.(C9H17N2O)c]m where a+b:c = 9:1 |
| Molar mass | variable |
| | |
Sevelamer (rINN) is a phosphate binding medication used to treat hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. When taken with meals, it binds to dietary phosphate and prevents its absorption. Sevelamer was invented and developed by GelTex Pharmaceuticals. Sevelamer is marketed by Sanofi under the brand names Renagel (sevelamer hydrochloride) and Renvela (sevelamer carbonate).
- ^ "Prescription medicines: registration of new chemical entities in Australia, 2015". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 June 2022. Retrieved 10 April 2023.
- ^ "Kidney disease". Health Canada. 9 May 2018. Retrieved 13 April 2024.
- ^ "Renvela EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 10 June 2009. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ "Renvela PI". Union Register of medicinal products. 12 June 2009. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ "Sevelamer carbonate Winthrop (previously Sevelamer carbonate Zentiva) EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 15 January 2015. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ "Sevelamer carbonate PI". Union Register of medicinal products. 19 January 2015. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ "Renagel EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 28 January 2000. Retrieved 5 September 2024.