| Sharpless epoxidation | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Karl Barry Sharpless |
| Reaction type | Ring forming reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| Organic Chemistry Portal | sharpless-epoxidation |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000141 |
The Sharpless epoxidation reaction is an enantioselective chemical reaction to prepare 2,3-epoxyalcohols from primary and secondary allylic alcohols. The oxidizing agent is tert-butyl hydroperoxide. The method relies on a catalyst formed from titanium tetra(isopropoxide) and diethyl tartrate.[1][2][3][4][5]
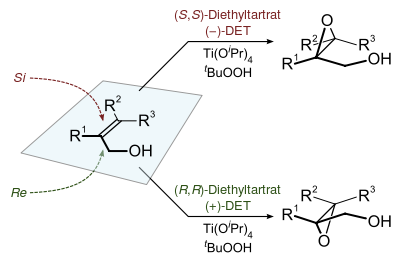
2,3-Epoxyalcohols can be converted into diols, aminoalcohols, and ethers. The reactants for the Sharpless epoxidation are commercially available and relatively inexpensive.[6] K. Barry Sharpless published a paper on the reaction in 1980 and was awarded the 2001 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this and related work on asymmetric oxidations. The prize was shared with William S. Knowles and Ryōji Noyori.
- ^ Diego J. Ramón and Miguel Yus (2006). "In the Arena of Enantioselective Synthesis, Titanium Complexes Wear the Laurel Wreath". Chem. Rev. 106 (6): 2126–2208. doi:10.1021/cr040698p. PMID 16771446.
- ^ Johnson, R. A.; Sharpless, K. B. (1991). "Addition Reactions with Formation of Carbon–Oxygen Bonds: (ii) Asymmetric Methods of Epoxidation". Compr. Org. Synth. 7: 389–436. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-052349-1.00196-7. ISBN 978-0-08-052349-1.
- ^ Hüft, E. (1993). "Enantioselective epoxidation with peroxidic oxygen". Top. Curr. Chem. Topics in Current Chemistry. 164: 63–77. doi:10.1007/3-540-56252-4_25. ISBN 978-3-540-56252-8.
- ^ Katsuki, T.; Martin, V. S. (1996). "Asymmetric Epoxidation of Allylic Alcohols: The Katsuki-Sharpless Epoxidation Reaction". Org. React. 48: 1–300. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or048.01. ISBN 0471264180.
- ^ Pfenninger, A. (1986). "Asymmetric Epoxidation of Allylic Alcohols: The Sharpless Epoxidation". Synthesis. 1986 (2): 89–116. doi:10.1055/s-1986-31489.
- ^ A. Pfenninger (1986). "Asymmetric Epoxidation of Allylic Alcohols: The Sharpless Epoxidation". Synthesis. 1986 (2): 88–116. doi:10.1055/s-1986-31489.