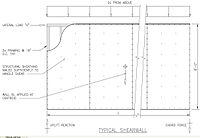
A shear wall is an element of a structurally engineered system that is designed to resist in-plane lateral forces, typically wind and seismic loads.
A shear wall resists loads parallel to the plane of the wall. Collectors, also known as drag members, transfer the diaphragm shear to shear walls and other vertical elements of the seismic force resisting system. Shear walls are typically made of light framed or braced wooden walls sheathed in shear-resisting material such as plywood or other structurally rigid panels, reinforced concrete, reinforced masonry, or steel plates.
While plywood is the conventional material used in wood (timber) shear walls, advances in technology and modern building methods have produced prefabricated options such as sheet steel and steel-backed shear panels used for narrow walls bracketing an opening that have proven to provide stronger seismic resistance.
In many jurisdictions, the International Building Code and International Residential Code govern the design of shear walls.