| Shtokavian | |
|---|---|
| štokavski / штокавски | |
| Native to | Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Kosovo |
Standard forms | |
| Dialects |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | sh |
| ISO 639-3 | hbs |
| Glottolog | shto1241 |
| Linguasphere | 53-AAA-ga to -gf & 53-AAA-gi (-gia to -gii) |
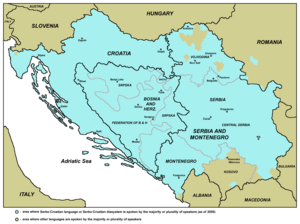
Shtokavian or Štokavian (/ʃtɒˈkɑːviən, -ˈkæv-/; Serbo-Croatian Latin: štokavski / Serbo-Croatian Cyrillic: штокавски, pronounced [ʃtǒːkaʋskiː])[1] is the prestige supradialect of the pluricentric Serbo-Croatian language and the basis of its Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian and Montenegrin standards.[2] It is a part of the South Slavic dialect continuum.[3][4] Its name comes from the form for the interrogative pronoun for "what" što (Western Shtokavian; it is šta in Eastern Shtokavian). This is in contrast to Kajkavian and Chakavian (kaj and ča also meaning "what").
Shtokavian is spoken in Serbia, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, much of Croatia, and the southern part of Austria's Burgenland. The primary subdivisions of Shtokavian are based on three principles: one is different accents whether the subdialect is Old-Shtokavian or Neo-Shtokavian, second is the way the old Slavic phoneme jat has changed (Ikavian, Ijekavian or Ekavian), and third is presence of Young Proto-Slavic isogloss (Schakavian or Shtakavian). Modern dialectology generally recognises seven Shtokavian subdialects.

- ^ "štókavskī". Hrvatski jezični portal. Retrieved 21 March 2015.
- ^ Sussex & Cubberly (2006:506) "The core of the modern literary languages and the major dialect area, is Shtokavian (što 'what'), which covers the rest of the area where Serbo-Croatian is spoken."
- ^ Crystal (1998:25)
- ^ Alexander (2000:4)