| Siberian ibex | |
|---|---|

| |
| Female and male at the Berlin Zoological Garden, Germany | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Bovidae |
| Subfamily: | Caprinae |
| Tribe: | Caprini |
| Genus: | Capra |
| Species: | C. sibirica
|
| Binomial name | |
| Capra sibirica Pallas, 1776
| |
| |
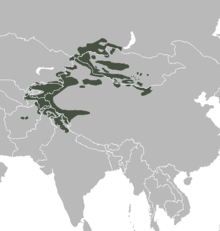
| Range of the Siberian ibex | |
The Siberian ibex (Capra sibirica), also known using regionalized names including Altai ibex, Asian ibex, Central Asian ibex, Gobi ibex, Himalayan ibex, Mongolian ibex or Tian Shan ibex,[2] is a polytypic species of ibex, a wild relative of goats and sheep. It lives in Central Asia, and is, by far, the most widely-distributed species in the genus Capra. In terms of population stability, Siberian ibex are currently ranked as Near Threatened, mostly due to over-hunting (mainly by wealthy, foreign hunters), low densities (in most areas) and overall decline; still, reliable data is minimal and difficult to come by, in addition to the animals’ expansive natural range, so accurate observations are still scant.[3] The Siberian ibex has, formerly, been treated as a subspecies of the Eurasian Alpine ibex, and whether or not it is a single species or a complex of distinct units that stand out as genetically-distinct (at species level) is still not entirely clear.[2][4] The Siberian ibex is the longest and heaviest member of the genus Capra, though its shoulder height is slightly surpassed by the markhor.
- ^ Reading, R.; Michel, S.; Suryawanshi, K.; Bhatnagar, Y.V. (2020). "Capra sibirica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T42398A22148720. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T42398A22148720.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ a b Sarasa, M. (2023-03-03). "Common names of the Asiatic ibex superspecies at a turning point in its taxonomy and management". Animal Biodiversity and Conservation (in Catalan): 79–86. doi:10.32800/abc.2023.46.0079. ISSN 2014-928X.
- ^ IUCN (2020-01-04). "Capra sibirica: Reading, R., Michel, S., Suryawanshi, K. & Bhatnagar, Y.V.: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020: e.T42398A22148720". doi:10.2305/iucn.uk.2020-2.rlts.t42398a22148720.en.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Dutt Joshi, B; Jabin, G; Sharief, A; Kumar, V; Mukherjee, T; Kumar, M; Singh, A; Kumar Singh, S; Chandra, K; Sharma, Lk; Thakur, M (2020-05-14). "Genetic evidence for allopatric speciation of the Siberian ibex Capra sibirica in India". Endangered Species Research. 42: 1–5. doi:10.3354/esr01034. ISSN 1863-5407.
