
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Silver(I) chloride
| |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.121 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| AgCl | |
| Molar mass | 143.32 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 5.56 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | 455 °C (851 °F; 728 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,547 °C (2,817 °F; 1,820 K) |
| 520 μg/100 g at 50 °C | |
Solubility product (Ksp)
|
1.77×10−10[1] |
| Solubility | soluble in NH3, conc. HCl, conc. H2SO4, alkali cyanide, (NH4)2CO3, KBr, Na2S2O3; |
| −49.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
2.071 |
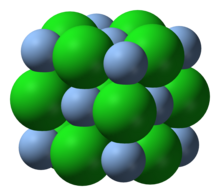
| Structure[2] | |
| cubic | |
| Fm3m (No. 225) | |
a = 555 pm
| |
| Octahedral | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
96 J·mol−1·K−1[3] |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−127 kJ·mol−1[3] |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Fischer Scientific, Salt Lake Metals |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
silver(I) fluoride, silver bromide, silver iodide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Silver chloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula AgCl. This white crystalline solid is well known for its low solubility in water and its sensitivity to light. Upon illumination or heating, silver chloride converts to silver (and chlorine), which is signaled by grey to black or purplish coloration in some samples. AgCl occurs naturally as the mineral chlorargyrite.
It is produced by a metathesis reaction for use in photography and in pH meters as electrodes.
- ^ John Rumble (June 18, 2018). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (99 ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–189. ISBN 978-1138561632.
- ^ S. Hull; D. A. Keen (1999). "Pressure-induced phase transitions in AgCl, AgBr, and AgI". Physical Review B. 59 (2). APS: 750–761. Bibcode:1999PhRvB..59..750H. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.59.750. S2CID 123044752.
- ^ a b Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A23. ISBN 978-0-618-94690-7.
