
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Silver tetrafluoridoborate(1–)
| |
| Other names
Borate(1-), tetrafluoro-, silver(1+)
Argentous tetrafluoroborate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.491 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| AgBF4 | |
| Molar mass | 194.673 g/mol |
| Appearance | Off-white powder |
| Odor | almost odorless |
| Density | 4.16 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 71.5 °C (160.7 °F; 344.6 K) (monohydrate) |
| soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
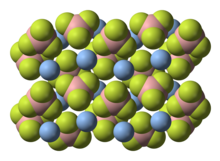
Silver tetrafluoroborate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula AgBF4. It is a white solid that dissolves in polar organic solvents as well as water. In its solid state, the Ag+ centers are bound to fluoride.[2]
- ^ "Silver tetrafluoroborate". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- ^ Evgeny Goreshnik, Zoran Mazej, "X-ray single crystal structure and vibrational spectra of AgBF4" Solid State Sciences 2005, Volume 7, pp. 1225–1229. doi:10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2005.06.007
