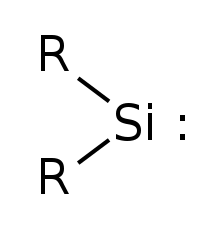
 Simplest silylene has R=Hydrogen
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Silylene
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Silylidene[1] | |
| Other names
Hydrogen silicide(−II)
Silicene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
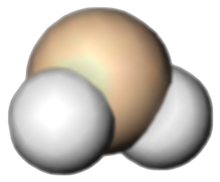
| H2Si | |
| Molar mass | 30.101 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Silylene is a chemical compound with the formula SiH2. It is the silicon analog of methylene, the simplest carbene. Silylene is a stable molecule as a gas but rapidly reacts in a bimolecular manner[clarification needed] when condensed. Unlike carbenes, which can exist in the singlet or triplet state, silylene (and all of its derivatives) are singlets.
Silylenes are formal derivatives of silylene with its hydrogens replaced by other substituents.[2] Most examples feature amido (NR2) or alkyl/aryl groups.[3][4] Silylenes have been proposed as reactive intermediates. They are carbene analogs.[5]
- ^ IUPAC Chemical Nomenclature and Structure Representation Division (2013). "P-71.2.2.1". In Favre, Henri A.; Powell, Warren H. (eds.). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. IUPAC–RSC. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Mizuhata, Yoshiyuki; Sasamori, Takahiro; Tokitoh, Norihiro (2009). "Stable Heavier Carbene Analogues". Chemical Reviews. 109 (8): 3479–3511. doi:10.1021/cr900093s. PMID 19630390.
- ^ Nagendran, Selvarajan; Roesky, Herbert W. (2008). "The Chemistry of Aluminum(I), Silicon(II), and Germanium(II)". Organometallics. 27 (4): 457–492. doi:10.1021/om7007869.
- ^ Haaf, Michael; Schmedake, Thomas A.; West, Robert (2000). "Stable Silylenes". Accounts of Chemical Research. 33 (10): 704–714. doi:10.1021/ar950192g. PMID 11041835.
- ^ Gaspar, Peter; West, R. (1998). "Silylenes". The Chemistry of Organic Silicon Compounds. The Chemistry of Functional Groups. Vol. 2. pp. 2463–2568. doi:10.1002/0470857250.ch43. ISBN 0471967572.