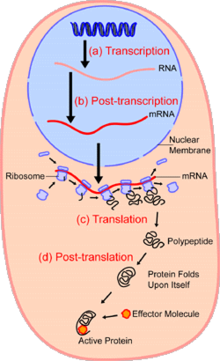
In cell biology, single-cell analysis and subcellular analysis[1] refer to the study of genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and cell–cell interactions at the level of an individual cell, as opposed to more conventional methods which study bulk populations of many cells.[2][3][4]
The concept of single-cell analysis originated in the 1970s. Before the discovery of heterogeneity, single-cell analysis mainly referred to the analysis or manipulation of an individual cell within a bulk population of cells under the influence of a particular condition using optical or electron microscopy.[5] Due to the heterogeneity seen in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell populations, analyzing the biochemical processes and features of a single cell makes it possible to discover mechanisms which are too subtle or infrequent to be detectable when studying a bulk population of cells; in conventional multi-cell analysis, this variability is usually masked by the average behavior of the larger population.[6] Technologies such as fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) allow the precise isolation of selected single cells from complex samples, while high-throughput single-cell partitioning technologies[7][8][9] enable the simultaneous molecular analysis of hundreds or thousands of individual unsorted cells; this is particularly useful for the analysis of variations in gene expression between genotypically identical cells, allowing the definition of otherwise undetectable cell subtypes.
The development of new technologies is increasing scientists' ability to analyze the genome and transcriptome of single cells,[10] and to quantify their proteome and metabolome.[11][12][13] Mass spectrometry techniques have become important analytical tools for proteomic and metabolomic analysis of single cells.[14][15] Recent advances have enabled the quantification of thousands of proteins across hundreds of single cells,[16] making possible new types of analysis.[17][18] In situ sequencing and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) do not require that cells be isolated and are increasingly being used for analysis of tissues.[19]
- ^ Siuzdak G (September 2023). "Subcellular quantitative imaging of metabolites at the organelle level". Nature Metabolism. 5 (9): 1446–1448. doi:10.1038/s42255-023-00882-z. PMID 37679555. S2CID 261607846.
- ^ Wang D, Bodovitz S (June 2010). "Single cell analysis: the new frontier in 'omics'". Trends in Biotechnology. 28 (6): 281–90. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2010.03.002. PMC 2876223. PMID 20434785.
- ^ Habibi I, Cheong R, Lipniacki T, Levchenko A, Emamian ES, Abdi A (April 2017). "Computation and measurement of cell decision making errors using single cell data". PLOS Computational Biology. 13 (4): e1005436. Bibcode:2017PLSCB..13E5436H. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005436. PMC 5397092. PMID 28379950.
- ^ Merouane A, Rey-Villamizar N, Lu Y, Liadi I, Romain G, Lu J, et al. (October 2015). "Automated profiling of individual cell-cell interactions from high-throughput time-lapse imaging microscopy in nanowell grids (TIMING)". Bioinformatics. 31 (19): 3189–97. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btv355. PMC 4693004. PMID 26059718.
- ^ Loo J, Ho H, Kong S, Wang T, Ho Y (September 2019). "Technological Advances in Multiscale Analysis of Single Cells in Biomedicine". Advanced Biosystems. 3 (11): e1900138. doi:10.1002/adbi.201900138. PMID 32648696. S2CID 203101696.
- ^ Altschuler SJ, Wu LF (May 2010). "Cellular heterogeneity: do differences make a difference?". Cell. 141 (4): 559–63. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.033. PMC 2918286. PMID 20478246.
- ^ Hu P, Zhang W, Xin H, Deng G (2016-10-25). "Single Cell Isolation and Analysis". Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 4: 116. doi:10.3389/fcell.2016.00116. PMC 5078503. PMID 27826548.
- ^ Mora-Castilla S, To C, Vaezeslami S, Morey R, Srinivasan S, Dumdie JN, et al. (August 2016). "Miniaturization Technologies for Efficient Single-Cell Library Preparation for Next-Generation Sequencing". Journal of Laboratory Automation. 21 (4): 557–67. doi:10.1177/2211068216630741. PMC 4948133. PMID 26891732.
- ^ Zheng GX, Terry JM, Belgrader P, Ryvkin P, Bent ZW, Wilson R, et al. (January 2017). "Massively parallel digital transcriptional profiling of single cells". Nature Communications. 8: 14049. Bibcode:2017NatCo...814049Z. doi:10.1038/ncomms14049. PMC 5241818. PMID 28091601.
- ^ Mercatelli D, Balboni N, Palma A, Aleo E, Sanna PP, Perini G, et al. (January 2021). "Single-Cell Gene Network Analysis and Transcriptional Landscape of MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma Cell Lines". Biomolecules. 11 (2): 177. doi:10.3390/biom11020177. PMC 7912277. PMID 33525507.
- ^ Huang L, Ma F, Chapman A, Lu S, Xie XS (2015). "Single-Cell Whole-Genome Amplification and Sequencing: Methodology and Applications". Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics. 16 (1): 79–102. doi:10.1146/annurev-genom-090413-025352. PMID 26077818. S2CID 12987987.
- ^ Wu AR, Wang J, Streets AM, Huang Y (June 2017). "Single-Cell Transcriptional Analysis". Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry. 10 (1): 439–462. doi:10.1146/annurev-anchem-061516-045228. PMID 28301747. S2CID 40069109.
- ^ Tsioris K, Torres AJ, Douce TB, Love JC (2014). "A new toolbox for assessing single cells". Annual Review of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. 5: 455–77. doi:10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-060713-035958. PMC 4309009. PMID 24910919.
- ^ Comi TJ, Do TD, Rubakhin SS, Sweedler JV (March 2017). "Categorizing Cells on the Basis of their Chemical Profiles: Progress in Single-Cell Mass Spectrometry". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 139 (11): 3920–3929. doi:10.1021/jacs.6b12822. PMC 5364434. PMID 28135079.
- ^ Zhang L, Vertes A (April 2018). "Single-Cell Mass Spectrometry Approaches to Explore Cellular Heterogeneity". Angewandte Chemie. 57 (17): 4466–4477. doi:10.1002/anie.201709719. PMID 29218763. S2CID 4928231.
- ^ Slavov N (June 2020). "Single-cell protein analysis by mass spectrometry". Current Opinion in Chemical Biology. 60: 1–9. arXiv:2004.02069. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2020.04.018. ISSN 1367-5931. PMC 7767890. PMID 32599342. S2CID 219966629.
- ^ Specht H, Slavov N (August 2018). "Transformative Opportunities for Single-Cell Proteomics". Journal of Proteome Research. 17 (8): 2565–2571. doi:10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00257. PMC 6089608. PMID 29945450.
- ^ Slavov N (January 2020). "Unpicking the proteome in single cells". Science. 367 (6477): 512–513. Bibcode:2020Sci...367..512S. doi:10.1126/science.aaz6695. PMC 7029782. PMID 32001644.
- ^ Lee JH (July 2017). "De Novo Gene Expression Reconstruction in Space". Trends in Molecular Medicine. 23 (7): 583–593. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2017.05.004. PMC 5514424. PMID 28571832.