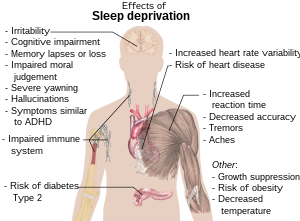
Sleep debt or sleep deficit is the cumulative effect of not getting enough sleep. A large sleep debt may lead to mental or physical fatigue, and can adversely affect one's mood, energy, and ability to think clearly.
There are two kinds of sleep debt: the result of partial sleep deprivation, and of total sleep deprivation. Partial sleep deprivation occurs when a person or a lab animal sleeps too little for several days or weeks. Total sleep deprivation, on the other hand, occurs when the subject is kept awake for at least 24 hours. There is debate in the scientific community over the specifics of sleep debt (see § Scientific debate), and it is not considered to be a disorder.[citation needed]
- ^ Reference list is found on image page on Wikimedia Commons: Commons:File:Effects of sleep deprivation.svg#References.