
Small wind turbines, also known as micro wind turbines or urban wind turbines, are wind turbines that generate electricity for small-scale use. These turbines are typically smaller than those found in wind farms. Small wind turbines often have passive yaw systems as opposed to active ones. They use a direct drive generator and use a tail fin to point into the wind, whereas larger turbines have geared powertrains that are actively pointed into the wind.
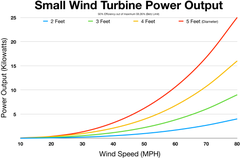
They usually produce between 500 W and 10 kW, with some as small as 50 W. The Canadian Wind Energy Association considers small wind turbines to be up to 300 kW,[1] while the IEC 61400 standard defines them as having a rotor area smaller than 200 m2 and generating voltage below 1000 Va.c. or 1500 Vd.c.
- ^ Small Wind Turbine Purchasing Guide (PDF) (Report). Canadian Wind Energy Association. pp. 3–4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 March 2013. Retrieved 1 March 2016.