| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
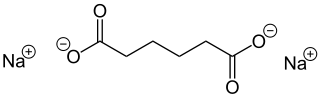
Disodium hexanedioate | |
| Other names
Disodium adipate
Adipic acid, sodium salt | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.448 |
| E number | E356 (antioxidants, ...) |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H8Na2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 190.106 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Solid white to off-white powder or crystals |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P305+P351+P338 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
4000 mg/kg (intraperitoneal, mouse) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | [1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Sodium adipate is a chemical organic compound with formula Na2C6H8O4. It is the sodium salt of adipic acid.
As a food additive, it has the E number E356 as is used as a buffering agent and as an acidity regulator.[1]
- ^ "E356 Sodium adipate". food-info.net.
