 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Myocrisin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Multum Consumer Information |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | High[1] |
| Elimination half-life | 6-25 days[1] |
| Excretion | Urine (60-90%), faeces (10-40%)[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.242 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
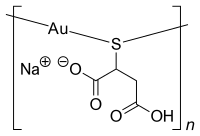
| Formula | C4H4AuNaO4S |
| Molar mass | 368.09 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Sodium aurothiomalate (INN, known in the United States as gold sodium thiomalate) is a gold compound that is used for its immunosuppressive anti-rheumatic effects.[2][3] Along with an orally-administered gold salt, auranofin, it is one of only two gold compounds currently employed in modern medicine.[4]
- ^ a b c "aurothiomalate, sodium, Myochrysine (gold sodium thiomalate) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Retrieved 13 March 2014.
- ^ Jessop JD, O'Sullivan MM, Lewis PA, Williams LA, Camilleri JP, Plant MJ, Coles EC (September 1998). "A long-term five-year randomized controlled trial of hydroxychloroquine, sodium aurothiomalate, auranofin and penicillamine in the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis". British Journal of Rheumatology. 37 (9): 992–1002. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/37.9.992. PMID 9783766.
- ^ Iqbal MS, Saeed M, Taqi SG (2008). "Erythrocyte membrane gold levels after treatment with auranofin and sodium aurothiomalate". Biological Trace Element Research. 126 (1–3): 56–64. doi:10.1007/s12011-008-8184-x. PMID 18649049. S2CID 20169992.
- ^ Kean WF, Kean IR (June 2008). "Clinical pharmacology of gold". Inflammopharmacology. 16 (3): 112–25. doi:10.1007/s10787-007-0021-x. PMID 18523733. S2CID 808858.