| |||
| |||
 Unit cell of sodium nitrite under standard conditions
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium nitrite
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.687 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E250 (preservatives) | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1500 3287 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
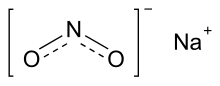
| NaNO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 68.9953 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | white or slightly yellowish crystalline solid | ||
| Density | 2.168 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 271 °C (520 °F; 544 K) (decomposes at 320 °C) | ||
| |||
| Solubility in methanol | 4.4 g/(100 mL) | ||
| Solubility in ethanol | Soluble | ||
| Solubility in diethyl ether | 0.3 g/(100 mL) | ||
| Solubility in ammonia | Very soluble | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | ~9 | ||
| −14.5·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.65 | ||
| Structure[1] | |||
| Orthorhombic | |||
| Im2m | |||
a = 3.5653(8) Å, b = 5.5728(7) Å, c = 5.3846(13) Å
| |||
Formula units (Z)
|
2 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
106 J/(mol·K) | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−359 kJ/mol[2] | ||
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
−295 kJ/mol | ||
| Pharmacology | |||
| V03AB08 (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling:[3] | |||
  
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H272, H301, H319, H400 | |||
| P220, P273, P301+P310, P305+P351+P338 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| 489 °C (912 °F; 762 K) | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
180 mg/kg (rats, oral) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | "Sodium nitrite". Safety Data Sheet. Sigma-Aldrich. 28 December 2022. | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
Sodium nitrate | ||
Other cations
|
|||
Related compounds
|
Nitrous acid | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Sodium nitrite is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaNO2. It is a white to slightly yellowish crystalline powder that is very soluble in water and is hygroscopic. From an industrial perspective, it is the most important nitrite salt. It is a precursor to a variety of organic compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, dyes, and pesticides, but it is probably best known as a food additive used in processed meats and (in some countries) in fish products.[4]
- ^ Gohda T, Ichikawa M (November 1996). "The Refinement of the Structure of Ferroelectric Sodium Nitrite". Journal of the Korean Physical Society. 29: 551–554.
- ^ Zumdahl SS (2009). Chemical Principles (6th ed.). Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A23. ISBN 978-0-618-94690-7.
- ^ "GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank sodium nitrite". gestis.dguv.de. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ Laue W, Thiemann M, Scheibler E, Wiegand KW (2006). "Nitrates and Nitrites". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_265. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.


