| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Disodium oxalate | |
| Other names
Oxalic acid, disodium salt
Sodium ethanedioate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.501 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
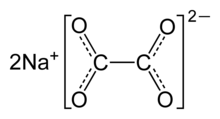
| Na2C2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 133.998 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 2.34 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 260 °C (500 °F; 533 K) decomposes above 290 °C[2] |
| |
| Solubility | Soluble in formic acid, insoluble in ethanol, diethyl ether |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−1318 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[3] | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H312 | |
| P280, P301+P312, P302+P352 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
11160 mg/kg (oral, rat)[1] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Oxford MSDS [unreliable source] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Sodium oxalate, or disodium oxalate, is a chemical compound with the chemical formula Na2C2O4. It is the sodium salt of oxalic acid. It contains sodium cations Na+ and oxalate anions C2O2−4. It is a white, crystalline, odorless solid, that decomposes above 290 °C.[2]
Sodium oxalate can act as a reducing agent, and it may be used as a primary standard for standardizing potassium permanganate (KMnO4) solutions.
The mineral form of sodium oxalate is natroxalate. It is only very rarely found and restricted to extremely sodic conditions of ultra-alkaline pegmatites.[4]
- ^ a b "ChemIDplus - 62-76-0 - ZNCPFRVNHGOPAG-UHFFFAOYSA-L - Disodium oxalate - Similar structures search, synonyms, formulas, resource links, and other chemical information". chem.nlm.nih.gov. NIH. Retrieved 7 January 2019.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
yoshiwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ GHS: GESTIS 570199
- ^ "Natroxolate" (PDF). RRUFF. Mineral Data Publishing. Retrieved 7 January 2019.
