| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
NaBH(OAc)3; STAB; STABH; Sodium triacetoxyhydroborate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.115.747 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
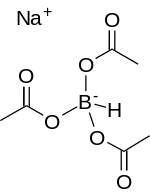
| Na[(CH3COO)3BH] | |
| Molar mass | 211.94 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Density | 1.20 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 116 to 120 °C (241 to 248 °F; 389 to 393 K) decomposes |
| decomposition | |
| Structure | |
| 4 at boron atom | |
| Tetrahedral at boron atom | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Sodium cyanoborohydride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Sodium triacetoxyborohydride, also known as sodium triacetoxyhydroborate, commonly abbreviated STAB, is a chemical compound with the formula Na[(CH3COO)3BH]. Like other borohydrides, it is used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis. This colourless salt is prepared by protonolysis of sodium borohydride with acetic acid:[1]
- Na[BH4] + 3 CH3COOH → Na[(CH3COO)3BH] + 3 H2
- ^ Gordon W. Gribble, Ahmed F. Abdel-Magid, "Sodium Triacetoxyborohydride" Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, 2007, John Wiley & Sons.doi:10.1002/047084289X.rs112.pub2
