 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Sovaldi, others[1] |
| Other names | PSI-7977; GS-7977 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a614014 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth[3] |
| Drug class | HCV polymerase inhibitor |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 92% |
| Protein binding | 61–65% |
| Metabolism | Quickly activated to triphosphate (CatA/CES1, HIST1, phosphorylation) |
| Elimination half-life | 0.4 hrs (sofosbuvir) 27 hrs (inactive metabolite GS-331007) |
| Excretion | 80% urine, 14% feces (mostly as GS-331007) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.224.393 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
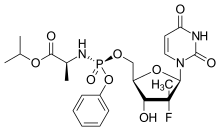
| Formula | C22H29FN3O9P |
| Molar mass | 529.458 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Sofosbuvir, sold under the brand name Sovaldi among others, is a medication used to treat hepatitis C.[3] It is taken by mouth.[3][6]
Common side effects include fatigue, headache, nausea, and trouble sleeping.[3] Side effects are generally more common in interferon-containing regimens.[7]: 7 Sofosbuvir may reactivate hepatitis B in those who have been previously infected.[9] In combination with ledipasvir, daclatasvir or simeprevir, it is not recommended with amiodarone due to the risk of an abnormally slow heartbeat.[7] Sofosbuvir is in the nucleotide analog family of medications and works by blocking the hepatitis C NS5B protein.[6]
Sofosbuvir was discovered in 2007 and approved for medical use in the United States in 2013.[7][10][11] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[12][13]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
EcTimes2015was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 16 December 2019. Retrieved 5 February 2020.
- ^ a b c d "Sofosbuvir". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 1 December 2016. Retrieved 30 November 2016.
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ "Prescription medicines: registration of new chemical entities in Australia, 2014". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 June 2022. Retrieved 10 April 2023.
- ^ a b c "Sovaldi 400 mg film coated tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics". UK Electronic Medicines Compendium. September 2016. Archived from the original on 10 November 2016. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ^ a b c d "Sovaldi- sofosbuvir tablet, film coated Sovaldi- sofosbuvir pellet". DailyMed. 27 September 2019. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- ^ "Sovaldi Access- sofosbuvir tablet, film coated". DailyMed. Retrieved 26 January 2022.
- ^ "Direct-Acting Antivirals for Hepatitis C: Drug Safety Communication - Risk of Hepatitis B Reactivating". FDA. 4 October 2016. Archived from the original on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 6 October 2016.
- ^ "Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) - Treatment - Hepatitis C Online". www.hepatitisc.uw.edu. Archived from the original on 23 December 2016. Retrieved 8 January 2017.
- ^ Gounder C (9 December 2013). "A Better Treatment for Hepatitis C". The New Yorker. Archived from the original on 20 September 2016.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ World Health Organization (2021). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/345533. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02.