| Solar eclipse of June 20, 1955 | |
|---|---|
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | −0.1528 |
| Magnitude | 1.0776 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 428 s (7 min 8 s) |
| Coordinates | 14°48′N 117°00′E / 14.8°N 117°E |
| Max. width of band | 254 km (158 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 4:10:42 |
| References | |
| Saros | 136 (34 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9410 |
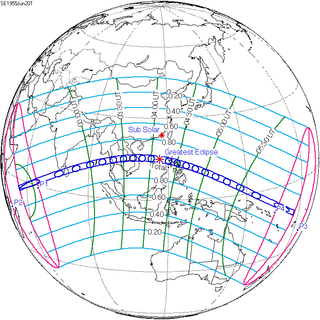
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Monday, June 20, 1955,[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12] with a magnitude of 1.0776. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 14.5 hours after perigee (on June 19, 1955, at 14:40 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.[13]
With a maximum duration of 7 minutes 7.74 seconds, this is the longest solar eclipse of Saros series 136, as well as the longest total solar eclipse since the 11th century, and until the 22nd century, because greatest eclipse occurred near the equator.[14]
Totality began over the Indian Ocean, British Seychelles (today's Seychelles) and Maldives, crossing Ceylon (name changed to Sri Lanka later) including the capital city Colombo, Andaman Islands, Burma, Thailand including the capital city Bangkok, Cambodia, Laos, South Vietnam (now belonging to Vietnam), Paracel Islands and Scarborough Shoal (near the greatest eclipse), moving across the Philippines including the capital city Manila, Kayangel Atoll in the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (now belonging to Palau), Nukumanu Islands in the Territory of Papua New Guinea (today's Papua New Guinea), towards northern Ontong Java Atoll in British Solomon Islands (today's Solomon Islands) ending over Southwestern Pacific Ocean. A partial eclipse was visible for parts of South Asia, Southeast Asia, East Asia, Australia, and Oceania.
This was the second of four central solar eclipses visible from Bangkok from 1948 to 1958, where it is extremely rare for a large city to witness four central solar eclipses within 10 years.
- ^ "June 20, 1955 Total Solar Eclipse". timeanddate. Retrieved 5 August 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Idaho State Journal 1955-06-21 p3was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
The Lexington Herald 1955-06-21 p1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
The World 1955-06-21 p11was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Troy Daily News 1955-06-20 p10was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
News Pilot 1955-06-20 p3was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Coventry Evening Telegraph 1955-06-20 p14was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Hull Daily Mail 1955-06-20 p5was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Birmingham Evening Mail 1955-06-20 p9was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Des Moines Tribune 1955-06-20 p3was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
The Boston Globe 1955-06-20 p8was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
The Berkshire Eagle 1955-06-20 p1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Moon Distances for London, United Kingdom, England". timeanddate. Retrieved 5 August 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
mivR6was invoked but never defined (see the help page).