| Solar eclipse of March 7, 1951 | |
|---|---|
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | −0.242 |
| Magnitude | 0.9896 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 59 s (0 min 59 s) |
| Coordinates | 17°42′S 123°30′W / 17.7°S 123.5°W |
| Max. width of band | 38 km (24 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
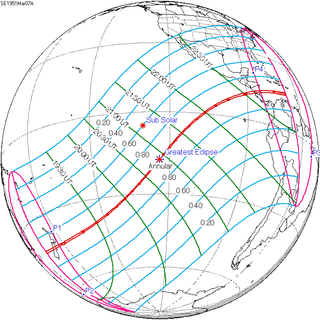
| Greatest eclipse | 20:53:40 |
| References | |
| Saros | 129 (48 of 80) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9400 |
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit between Wednesday, March 7 and Thursday, March 8, 1951,[1] with a magnitude of 0.9896. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The Moon's apparent diameter was near the average diameter because it occurred 5.5 days after perigee (on March 2, 1951, at 7:10 UTC) and 7.4 days before apogee (on March 15, 1951, at 6:20 UTC).[2]
Annularity was visible from New Zealand on March 8 (Thursday), and northern Costa Rica, Nicaragua, and San Andrés Island in Colombia on March 7 (Wednesday). A partial eclipse was visible for parts of Oceania, western South America, southern North America, Central America, and the Caribbean.
- ^ "March 7, 1951 Annular Solar Eclipse". timeanddate. Retrieved 5 August 2024.
- ^ "Moon Distances for London, United Kingdom, England". timeanddate. Retrieved 5 August 2024.