| Solar eclipse of November 19, 1816 | |
|---|---|
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.8408 |
| Magnitude | 1.0233 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 120 s (2 min 0 s) |
| Coordinates | 35°00′N 41°30′E / 35°N 41.5°E |
| Max. width of band | 144 km (89 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 10:17:23 |
| References | |
| Saros | 120 (50 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9081 |
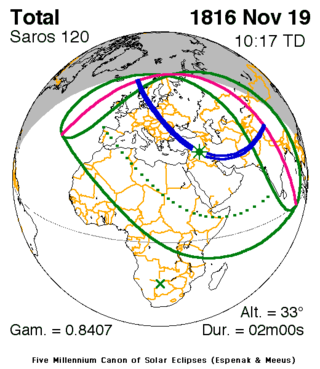
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Tuesday, November 19, 1816, with a magnitude of 1.0233. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 1.7 days before perigee (on November 17, 1816, at 17:10 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.[1]
The path of totality was visible from parts of modern-day Norway, Sweden, Poland, western Ukraine, Romania, Turkey, Syria, Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, northern India, and western China. A partial solar eclipse was also visible for parts of Europe, North Africa, Northeast Africa, the Middle East, Central Asia, and South Asia.
- ^ "Moon Distances for London, United Kingdom, England". timeanddate. Retrieved 22 September 2024.