| Solar eclipse of October 23, 1957 | |
|---|---|
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 1.0022 |
| Magnitude | 1.0013 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | - |
| Coordinates | 71°12′S 23°06′W / 71.2°S 23.1°W |
| Max. width of band | - km |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 4:54:02 |
| References | |
| Saros | 123 (50 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9415 |
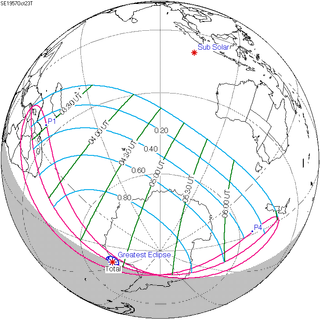
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Wednesday, October 23, 1957,[1] with a magnitude of 1.0013. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 1.4 days after perigee (on October 21, 1957, at 13:10 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.[2]
It was unusual that while it is a total solar eclipse, it is not a central one. A non-central eclipse is one where the center-line of totality does not intersect the surface of the Earth (when the gamma is between 0.9972 and 1.0260). Instead, the center line passes just above the Earth's surface. This rare type occurs when totality is only visible at sunset or sunrise in a polar region.
While totality was not visible for any land masses, a partial eclipse was visible for Southern Africa, Antarctica, and New Zealand. This was the last of 44 umbral solar eclipses in Solar Saros 123.
- ^ "October 23, 1957 Total Solar Eclipse". timeanddate. Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ "Moon Distances for London, United Kingdom, England". timeanddate. Retrieved 6 August 2024.