 Aerial view of islands in Solomon Archipelago | |
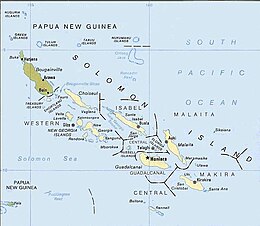 The Solomon Islands archipelago | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Pacific Ocean |
| Coordinates | 9°28′S 159°49′E / 9.467°S 159.817°E |
| Archipelago | Solomon Islands archipelago |
| Total islands | 6 main islands and more than 986 smaller islands |
| Major islands | Bougainville, Choiseul, the New Georgia Islands, Santa Isabel, Malaita, Makira (San Cristobal), Guadalcanal. |
| Administration | |
The Solomon Archipelago is a terrestrial ecoregion and marine ecoregion in the Pacific Ocean. It includes the tropical ocean waters surrounding most of the Solomon Islands archipelago (excluding the Santa Cruz Islands, which is a part of the Vanuatu marine ecoregion with the forests being part of the Vanuatu rain forests ecoregion), and includes Bougainville Island and Buka Island of Papua New Guinea and their surrounding waters.
Bougainville is the largest island in the archipelago, while it is geographically part of the Solomon Archipelago, it is politically an autonomous region of Papua New Guinea.
The Solomon Islands rain forests form part of the East Melanesian Islands ecoregion, also known as the Solomons-Vanuatu-Bismarck moist forests, which is a biogeographic region in the Melanesia subregion of Oceania.[1]
- ^ Dinerstein, Eric; et al. (2017). "An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm". BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.