| Somali | |
|---|---|
| Af Soomaali,[1] Soomaali[2] 𐒖𐒍 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘, 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘 اف صومالِ, صومالِ, | |
| Pronunciation | [af soːmaːli] |
| Region | Horn of Africa |
| Ethnicity | Somalis |
Native speakers | 24 million (2019–2023)[3] |
| Dialects | |
| Somali Latin alphabet (Latin script; official) Wadaad's writing (Arabic script) Osmanya alphabet Borama alphabet Kaddare alphabet | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | Regional Somali Language Academy |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | so |
| ISO 639-2 | som |
| ISO 639-3 | som |
| Glottolog | soma1255 |
| Linguasphere | 14-GAG-a |
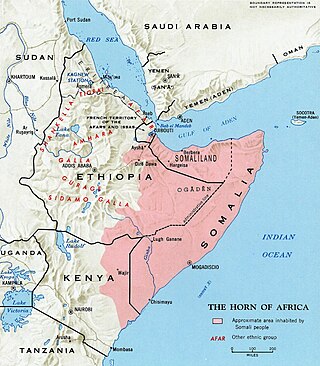 Primary Somali Sprachraum | |
Somali (/səˈmɑːli, soʊ-/ sə-MAH-lee, soh-;[4][5] Latin script: Af Soomaali; Wadaad: اف صومالِ; Osmanya: 𐒖𐒍 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘 [af soːmaːli])[6] is an Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic branch. It is spoken primarily in Greater Somalia, and by the Somali diaspora as a mother tongue. Somali is an official language in both Somalia and Ethiopia,[7] and serves as a national language in Djibouti, it is also a recognised minority language in Kenya. The Somali language is officially written with the Latin alphabet although the Arabic script and several Somali scripts like Osmanya, Kaddare and the Borama script are informally used.[8][9]
- ^ "Somali alphabets, pronunciation and language". Omniglot. Retrieved 16 June 2017.
- ^ "cldr/so.xml at master · unicode-org/cldr". Unicode. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
ethwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Jones, Daniel (2003) [1917], Peter Roach; James Hartmann; Jane Setter (eds.), English Pronouncing Dictionary, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 3-12-539683-2
- ^ "Somali". Collins Dictionary. Retrieved 21 September 2013.
- ^ Saeed (1999:107)
- ^ AfricaNews (2020-03-04). "One to five: Ethiopia gets four new federal working languages". Africanews. Archived from the original on 2020-10-28. Retrieved 2021-11-11.
- ^ Lewis, I.M. (1999). A Pastoral Democracy: A Study of Pastoralism and Politics Among the Northern Somali of the Horn of Africa. LIT Verlag Münster. p. 175. ISBN 3825830845.
- ^ Lewis, I.M. (1958), The Gadabuursi Somali Script, Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London, Vol. 21, pp. 134–156.