 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nexavar, others |
| Other names | Sorafenib tosylate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607051 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 38–49% |
| Protein binding | 99.5% |
| Metabolism | Liver oxidation and glucuronidation (CYP3A4 & UGT1A9-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 25–48 hours |
| Excretion | Feces (77%) and urine (19%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.110.083 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
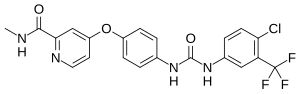
| Formula | C21H16ClF3N4O3 |
| Molar mass | 464.83 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Sorafenib, sold under the brand name Nexavar,[3] is a kinase inhibitor drug approved for the treatment of primary kidney cancer (advanced renal cell carcinoma), advanced primary liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma), FLT3-ITD positive AML and radioactive iodine resistant advanced thyroid carcinoma.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Nexavar FDA labelwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Nexavar EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 14 October 2021. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- ^ "FDA Approves Nexavar for Patients with Inoperable Liver Cancer" (Press release). FDA. 19 November 2007. Archived from the original on 2 January 2017. Retrieved 10 November 2012.