| Sotos syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Cerebral gigantism or Sotos-Dodge syndrome |
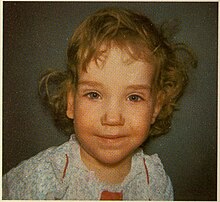 | |
| Girl displaying characteristic facial features of Sotos syndrome | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Sotos syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by excessive physical growth during the first years of life. Excessive growth often starts in infancy and continues into the early teen years. The disorder may be accompanied by autism,[1] mild intellectual disability, delayed motor, cognitive, and social development, hypotonia (low muscle tone), and speech impairments. Children with Sotos syndrome tend to be large at birth and are often taller, heavier, and have relatively large skulls (macrocephaly) than is normal for their age. Signs of the disorder, which vary among individuals, include a disproportionately large skull with a slightly protrusive forehead, large hands and feet, large mandible, hypertelorism (an abnormally increased distance between the eyes), and downslanting eyes. Clumsiness, an awkward gait, and unusual aggressiveness or irritability may also occur.
Although most cases of Sotos syndrome occur sporadically, familial cases have also been reported. It is similar to Weaver syndrome.
- ^ "Exploring Autism". www.exploringautism.org. Archived from the original on 2002-08-11.