| South Saskatchewan River | |
|---|---|
 The University Bridge over the South Saskatchewan River at Saskatoon | |
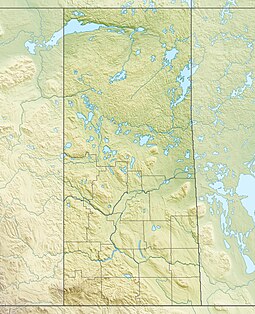
 The South Saskatchewan River drainage basin | |
| Location | |
| Country | Canada |
| Provinces | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source confluence | Oldman and Bow Rivers |
| • location | Municipal District of Taber, Alberta |
| • coordinates | 49°56′00″N 111°41′30″W / 49.93333°N 111.69167°W |
| • elevation | 700 m (2,300 ft) |
| Mouth | Saskatchewan River |
• location | Saskatchewan River Forks, Saskatchewan |
• coordinates | 53°14′6″N 105°4′58″W / 53.23500°N 105.08278°W |
• elevation | 380 m (1,250 ft) |
| Length | 1,392 km (865 mi) |
| Basin size | 146,100 km2 (56,400 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Saskatoon, SK |
| • average | 249 m3/s (8,800 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | |
| • right | |
The South Saskatchewan River[1] is a major river in the Canadian provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan. The river begins at the confluence of the Bow and Oldman Rivers in southern Alberta and ends at the Saskatchewan River Forks in central Saskatchewan. The Saskatchewan River Forks is the confluence of the South and North Saskatchewan Rivers and is the beginning of the Saskatchewan River.
For the first half of the 20th century, the South Saskatchewan would completely freeze over during winter, creating spectacular ice breaks and dangerous conditions in Saskatoon, Medicine Hat, and elsewhere. At least one bridge in Saskatoon was destroyed by ice carried by the river. The construction of the Gardiner Dam in the 1960s, however, lessened the power of the river by diverting a substantial portion of the South Saskatchewan's natural flow into the Qu'Appelle River. By the 1980s many permanent sandbars had formed due to the lowering of the level of the river.
From the headwaters of the Bow River, the South Saskatchewan flows for 1,392 kilometres (865 mi). At its mouth at Saskatchewan River Forks, it has an average discharge of 280 cubic metres per second (9,900 cu ft/s) and has a watershed of 146,100 square kilometres (56,400 sq mi), 1,800 of which are in Montana in the United States and 144,300 square kilometres (55,700 sq mi) in Alberta and Saskatchewan.[2]
- ^ "South Saskatchewan River". Canadian Geographical Names Database. Government of Canada. Retrieved 2 March 2023.
- ^ Atlas of Canada. "Rivers in Canada". Retrieved 1 May 2007.
(Webpage shows that the South Saskatchewan River has a much higher flow than the Saskatchewan River. But since the South is a tributary of the Saskatchewan River, it must be assumed that the data is reversed.)