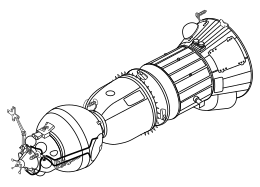
 Lunniy Orbitalny Korabl drawing | |
| Manufacturer | OKB-1 |
|---|---|
| Designer | Sergei Korolev |
| Country of origin | Soviet Union |
| Operator | Soviet space program |
| Applications | Crewed cislunar flight and lunar orbit |
| Specifications | |
| Launch mass | 9,850 kilograms (21,720 lb) |
| Crew capacity | 2 |
| Dimensions | 10.06 meters (33.0 ft) length 2.93 meters (9.6 ft) diameter |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit Cislunar space Lunar orbit |
| Production | |
| Status | Canceled |
| Built | 6 |
| Launched | 5 |
| Failed | 4 |
| Maiden launch | December 2, 1970 |
| Last launch | November 23, 1972 |
| Related spacecraft | |
| Derived from | Soyuz 7K-OK |
| Derivatives | Soyuz 7K-L1 lunar flyby Soyuz 7K-OKS space station shuttle |
| Flown with | LK lander |

The Soyuz 7K-LOK, or simply LOK (Russian: Лунный Орбитальный Корабль, romanized: Lunniy Orbitalny Korabl meaning "Lunar Orbital Craft") was a Soviet crewed spacecraft designed to take humans from Earth to orbit the Moon, developed in parallel to the 7K-L1. The LOK would carry two cosmonauts, acting as a mother ship for the LK lander which would land one crew member to the surface. It was part of the N1-L3 programme which also included the LK lander and the N1 rocket.[1]
- ^ Wade, Mark. "L3". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 1 December 2012. Retrieved 5 July 2011.