 Soyuz 7K-OK (active) spacecraft with an active docking unit | |
| Manufacturer | Experimental Design Bureau (OKB-1) |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | Soviet Union |
| Operator | Soviet space program |
| Applications | Tested a new crewed space vehicle in orbit and returned to Earth |
| Specifications | |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Production | |
| Status | No longer in service |
| Built | 16 |
| Launched | 16 |
| Maiden launch | Kosmos 133, 1966 |
| Last launch | Soyuz 9, 1970 |
| Related spacecraft | |
| Derived from | Soyuz-A (concept only) |
| Derivatives | Soyuz 7K-OKS (Salyut 1 ferry)
Soyuz 7K-L1[1] (lunar) Soyuz 7K-LOK[citation needed] (lunar) Soyuz 7K-T (successor) |
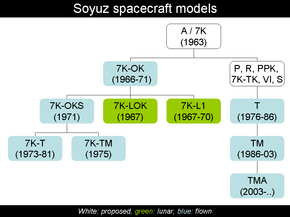
Soyuz 7K-OK was the first generation of Soyuz spacecraft and was flown between 1967 and 1971.[2] The 7K-OK was used for the first ferry flights to the Salyut space station program, beginning a long history of space station service that continues with the International Space Station (ISS).
As of 2024[update], the 7K-OK was responsible for the only fatalities of the Soyuz programme, with Soyuz 1 in 1967 (sole crew-member killed by parachute failure) and Soyuz 11 in 1971 (three crew killed by depressurisation during reentry).
The first uncrewed automated docking in the history of spaceflight was achieved between 7K-OK spacecraft Kosmos 186 and Kosmos 188 in 1967. Additional firsts include the first docking between two crewed spacecraft (Soyuz 4 and Soyuz 5), the longest crewed flight involving only one spacecraft (the 18-day flight of Soyuz 9 in 1970), and the first successful transfer of crew to the first space station in the history of space flight (Soyuz 11 and Salyut 1 in 1971).
- ^ Siddiqi, Asif (March 2003). Simpson, Clive; Owens, Lucy (eds.). "Soyuz variants: a 40-year history" (PDF). British Interplanetary Society. 45 (3): 119.
- ^ Portree, David (March 1995). "Mir Hardware Heritage" (PDF). NASA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 September 2009. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.