 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
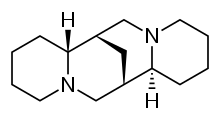
| Other names | (6R,8S,10R,12S)-7,15-diazatetracyclo[7.7.1.02,7.010,15]heptadecane |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.808 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H26N2 |
| Molar mass | 234.387 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.02 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 30 °C (86 °F) |
| Boiling point | 325 °C (617 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 3.04 mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| | |
Sparteine is a class 1a antiarrhythmic agent and sodium channel blocker. It is an alkaloid and can be extracted from scotch broom. It is the predominant alkaloid in Lupinus mutabilis, and is thought to chelate the bivalent metals calcium and magnesium. It is not FDA approved for human use as an antiarrhythmic agent, and it is not included in the Vaughan Williams classification of antiarrhythmic drugs.
It is also used as a chiral ligand in organic chemistry, especially in syntheses involving organolithium reagents.