 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Trobicin |
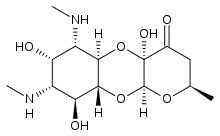
| Other names | (2R,4aR,5aR,6S,7S,8R,9S,9aR,10aS)-4a,7,9-trihydroxy-2-methyl-6,8-bis(methylamino)decahydro-4H-pyrano[2,3-b][1,4]benzodioxin-4-one , SPT/SPE/SC/SP[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Routes of administration | IM |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.374 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H24N2O7 |
| Molar mass | 332.353 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 184 to 194 °C (363 to 381 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Spectinomycin, sold under the tradename Trobicin among others, is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of gonorrhea infections.[2] It is given by injection into a muscle.[2]
Common side effects include pain at the area of injection, rash, nausea, fever, and trouble sleeping.[2] Severe allergic reactions may occasionally occur.[2] It is generally safe to use during pregnancy.[2] It may be used by those who are allergic to penicillin or cephalosporins.[2] It is in the aminocyclitol class of drugs and works by stopping the making of protein by certain bacteria.[2]
Spectinomycin was discovered in 1961.[3] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[4] It is not available in the United States for human use.[2] It is made from the bacterium Streptomyces spectabilis.[2]
- ^ "Antibiotic abbreviations list". Retrieved 22 June 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Spectinomycin Hydrochloride". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 2015-09-24. Retrieved Sep 6, 2015.
- ^ Textbook of Drug Design and Discovery, Fourth Edition. CRC Press. 2009. p. 438. ISBN 9781439882405. Archived from the original on 2015-10-03.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.