
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Strontium oxide
| |
| Other names
Strontia
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.837 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| SrO | |
| Molar mass | 103.619 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless cubic crystals |
| Density | 4.70 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 2,531 °C (4,588 °F; 2,804 K) |
| Boiling point | 3,200 °C (5,790 °F; 3,470 K) (decomposes) |
| reacts, forms Sr(OH)2 | |
| Solubility | miscible with potassium hydroxide slightly soluble in alcohol insoluble in acetone and ether |
| −35.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.810 [2] |
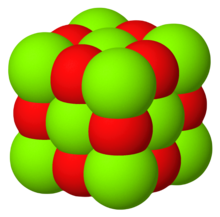
| Structure | |
| Halite (cubic), cF8 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
| Octahedral (Sr2+); octahedral (O2−) | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
44.3 J·mol−1·K−1 |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
57.2 J·mol−1·K−1 |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-592.0 kJ·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Strontium sulfide |
Other cations
|
Beryllium oxide Magnesium oxide Calcium oxide Barium oxide |
Related compounds
|
Strontium hydroxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Strontium oxide or strontia, SrO, is formed when strontium reacts with oxygen. Burning strontium in air results in a mixture of strontium oxide and strontium nitride. It also forms from the decomposition of strontium carbonate SrCO3. It is a strongly basic oxide.
- ^ Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. pp. 4–87. ISBN 0-8493-0594-2.
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-8