| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.841 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| SrO2 | |
| Molar mass | 119.619 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 4.56 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 1.91 g/cm3 (octahydrate) |
| Melting point | 215 °C (419 °F; 488 K) (decomposes)[1] |
| slightly soluble | |
| Solubility | very soluble in alcohol, ammonium chloride insoluble in acetone |
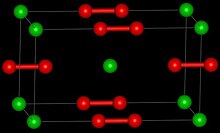
| Structure | |
| Tetragonal [2] | |
| D174h, I4/mmm, tI6 | |
| 6 | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   [3] [3]
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H312, H317, H331, H350 | |
| P220, P261, P280, P305+P351+P338 | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External SDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Strontium peroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Sr O2 that exists in both anhydrous and octahydrate form, both of which are white solids. The anhydrous form adopts a structure similar to that of calcium carbide.[4][5]
- ^ Middleburgh, Simon C.; Lagerlof, Karl Peter D.; Grimes, Robin W. (2013). "Accommodation of Excess Oxygen in Group II Monoxides". Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 96: 308–311. doi:10.1111/j.1551-2916.2012.05452.x.
- ^ Massalimov, I. A.; Kireeva, M. S.; Sangalov, Yu. A. (2002). "Structure and Properties of Mechanically Activated Barium Peroxide". Inorganic Materials. 38 (4): 363–366. doi:10.1023/A:1015105922260. S2CID 91881752.
- ^ "Strontium Peroxide". American Elements. Retrieved March 7, 2019.
- ^ Bernal, J. D.; D'yatlova, E.; Kasarnovskii, I.; Raikhstein, S. I.; Ward, A. G. "The structure of strontium and barium peroxides" Zeitschrift für Kristallographie, Kristallgeometrie, Kristallphysik, Kristallchemie (1935), 92, 344-54.
- ^ Natta, G. "Structure of hydroxides and hydrates. IV. Octahydrated strontium peroxide" Gazzetta Chimica Italiana (1932), 62, 444-56.