| tachykinin, precursor 1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Spacefilling model of substance P | |||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | TAC1 | ||||||
| Alt. symbols | TAC2, NKNA | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 6863 | ||||||
| HGNC | 11517 | ||||||
| OMIM | 162320 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_003182 | ||||||
| UniProt | P20366 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| Locus | Chr. 7 q21-q22 | ||||||
| |||||||
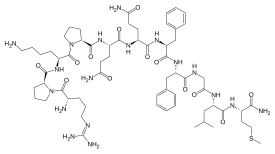
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.046.845 |
| MeSH | Substance+P |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C63H98N18O13S | |
| Molar mass | 1347.63 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Substance P (SP) is an undecapeptide (a peptide composed of a chain of 11 amino acid residues)[1] and a type of neuropeptide, belonging to the tachykinin family of neuropeptides. It acts as a neurotransmitter and a neuromodulator.[2][3] Substance P and the closely related neurokinin A (NKA) are produced from a polyprotein precursor after alternative splicing of the preprotachykinin A gene. The deduced amino acid sequence of substance P is as follows:[4]
with an amide group at the C-terminus.[5] Substance P is released from the terminals of specific sensory nerves. It is found in the brain and spinal cord and is associated with inflammatory processes and pain.
- ^ "Undecapeptide Definition & Meaning". Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 17 November 2022.
- ^ Harrison S, Geppetti P (Jun 2001). "Substance p". The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 33 (6): 555–76. doi:10.1016/S1357-2725(01)00031-0. PMID 11378438.
- ^ Datar P, Srivastava S, Coutinho E, Govil G (2004). "Substance P: structure, function, and therapeutics". Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 4 (1): 75–103. doi:10.2174/1568026043451636. PMID 14754378. Archived from the original on 2009-08-17. Retrieved 2008-11-01.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Reece JB, Campbell NA (2005). Biology, 7th Edition. San Francisco: Pearson, Benjamin Cummings. ISBN 9780805371468. OCLC 57368924.
- ^ Wong M, Jeng AY (Jan 1994). "Posttranslational modification of glycine-extended substance P by an alpha-amidating enzyme in cultured sensory neurons of dorsal root ganglia". Journal of Neuroscience Research. 37 (1): 97–102. doi:10.1002/jnr.490370113. PMID 7511706. S2CID 31252390.