| Supplementary motor area | |
|---|---|
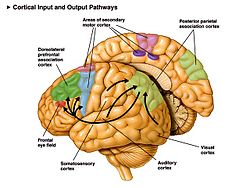 Some motor areas in the human cortex. The supplementary motor area is shown in pink. | |
 3D visualization of the supplementary motor cortex in an average human brain | |
| Identifiers | |
| NeuroNames | 3176 |
| FMA | 224858 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The supplementary motor area (SMA) is a part of the motor cortex of primates that contributes to the control of movement. It is located on the midline surface of the hemisphere just in front of (anterior to) the primary motor cortex leg representation. In monkeys, the SMA contains a rough map of the body. In humans, the body map is not apparent. Neurons in the SMA project directly to the spinal cord and may play a role in the direct control of movement. Possible functions attributed to the SMA include the postural stabilization of the body, the coordination of both sides of the body such as during bimanual action, the control of movements that are internally generated rather than triggered by sensory events, and the control of sequences of movements. All of these proposed functions remain hypotheses. The precise role or roles of the SMA is not yet known.
For the discovery of the SMA and its relationship to other motor cortical areas, see the main article on the motor cortex.