| Part of a series on |
| Research |
|---|
 |
| Philosophy portal |
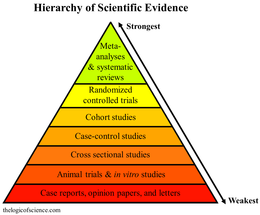
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic.[1] A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on the topic (in the scientific literature), then analyzes, describes, critically appraises and summarizes interpretations into a refined evidence-based conclusion.[1][2] For example, a systematic review of randomized controlled trials is a way of summarizing and implementing evidence-based medicine.[3]
While a systematic review may be applied in the biomedical or health care context, it may also be used where an assessment of a precisely defined subject can advance understanding in a field of research.[4] A systematic review may examine clinical tests, public health interventions, environmental interventions,[5] social interventions, adverse effects, qualitative evidence syntheses, methodological reviews, policy reviews, and economic evaluations.[6][7]
Systematic reviews are closely related to meta-analyses, and often the same instance will combine both (being published with a subtitle of "a systematic review and meta-analysis"). The distinction between the two is that a meta-analysis uses statistical methods to induce a single number from the pooled data set (such as an effect size), whereas the strict definition of a systematic review excludes that step. However, in practice, when one is mentioned, the other may often be involved, as it takes a systematic review to assemble the information that a meta-analysis analyzes, and people sometimes refer to an instance as a systematic review, even if it includes the meta-analytical component.
An understanding of systematic reviews and how to implement them in practice is common for professionals in health care, public health, and public policy.[1]
Systematic reviews contrast with a type of review often called a narrative review. Systematic reviews and narrative reviews both review the literature (the scientific literature), but the term literature review without further specification refers to a narrative review.
- ^ a b c "What is a systematic review?". Temple University Libraries. 6 June 2022. Retrieved 15 June 2022.
- ^ Armstrong R, Hall BJ, Doyle J, Waters E (March 2011). "Cochrane Update. 'Scoping the scope' of a cochrane review". Journal of Public Health. 33 (1): 147–150. doi:10.1093/pubmed/fdr015. PMID 21345890.
- ^ "What is EBM?". Centre for Evidence Based Medicine. 20 November 2009. Archived from the original on 6 April 2011. Retrieved 17 June 2011.
- ^ Ader HJ, Mellenbergh GJ, Hand DJ (2008). "Methodological quality". Advising on Research Methods: A consultant's companion. Johannes van Kessel Publishing. ISBN 978-90-79418-02-2.
- ^ Bilotta GS, Milner AM, Boyd I (2014). "On the use of systematic reviews to inform environmental policies". Environmental Science & Policy. 42: 67–77. Bibcode:2014ESPol..42...67B. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2014.05.010.
- ^ Systematic reviews: CRD's guidance for undertaking reviews in health care (PDF). York: University of York, Centre for Reviews and Dissemination. 2008. ISBN 978-1-900640-47-3. Retrieved 17 June 2011.
- ^ Petticrew M, Roberts H (2006). Systematic reviews in the social sciences (PDF). Wiley Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-2110-1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 June 2015.