| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
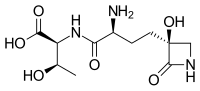
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S,3R)-2-{(2S)-2-Amino-4-[(3S)-3-hydroxy-2-oxoazetidin-3-yl]butanamido}-3-hydroxybutanoic acid | |
| Other names
N-[(2S)-2-Amino-4-[(3S)-3-hydroxy-2-oxo-3-azetidinyl]-1-oxobutyl]-L-threonine; (S)-γ-(3-Hydroxy-2-oxo-3-azetidinyl)-L-α-aminobutyryl-L-threonine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H19N3O6 | |
| Molar mass | 289.288 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tabtoxin, also known as wildfire toxin, is a simple monobactam phytotoxin produced by Pseudomonas syringae. It is the precursor to the antibiotic tabtoxinine β-lactam (TBL).[1] It is produced by:
- Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci, the causal agent of the wildfire of tobacco.
- P. syringae pv. coronafaciens
- P. syringae pv. garcae
- P. syringae BR2, causes a disease of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) similar to tobacco wildfire. This organism is closely related to P. syringae pv. tabaci but cannot be classified in the pathovar tabaci because it is not pathogenic on tobacco.
Tabtoxin is a dipeptide precursor to the biologically active form of TBL, differing by having an extra threonine attached by a peptide bond to the C terminus. Tabtoxin is required by BR2(R) for both chlorosis and lesion formation on bean. All mutations that affected tabtoxin production, whether spontaneous deletion or transposon induced, also affected lesion formation, and in all cases, restoration of tabtoxin production also restored pathogenic symptoms. Other factors may be required for BR2 to be pathogenic on bean, but apparently these are in addition to tabtoxin production.[2][3] TBL functions as a toxin by inhibition of glutamine synthetase.
- ^ Kinscherf TG, Coleman RH, Barta TM, Willis DK (July 1991). "Cloning and expression of the tabtoxin biosynthetic region from Pseudomonas syringae". J. Bacteriol. 173 (13): 4124–32. doi:10.1128/jb.173.13.4124-4132.1991. PMC 208062. PMID 1648077.
- ^ Arai, Toshinobu; Arimura, Yasuhiro; Ishikura, Shun; Kino, Kuniki (15 August 2013). "l-Amino Acid Ligase from Pseudomonas syringae Producing Tabtoxin Can Be Used for Enzymatic Synthesis of Various Functional Peptides". Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 79 (16): 5023–5029. Bibcode:2013ApEnM..79.5023A. doi:10.1128/AEM.01003-13. PMC 3754701. PMID 23770908.
- ^ Kinscherf, T. G.; Coleman, R. H.; Barta, T. M.; Willis, D. K. (1 July 1991). "Cloning and expression of the tabtoxin biosynthetic region from Pseudomonas syringae". Journal of Bacteriology. 173 (13): 4124–4132. doi:10.1128/jb.173.13.4124-4132.1991. PMC 208062. PMID 1648077.