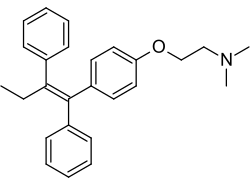
Tamoxifen, sold under the brand name Nolvadex among others, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator used to prevent breast cancer in women and men.[13] It is also being studied for other types of cancer.[13] It has been used for Albright syndrome.[14] Tamoxifen is typically taken daily by mouth for five years for breast cancer.[14]
Serious side effects include a small increased risk of uterine cancer, stroke, vision problems, and pulmonary embolism.[14] Common side effects include irregular periods, weight loss, and hot flashes.[14] It may cause harm to the baby if taken during pregnancy or breastfeeding.[14] It is a selective estrogen-receptor modulator (SERM) and works by decreasing the growth of breast cancer cells.[14][15] It is a member of the triphenylethylene group of compounds.[16]
Tamoxifen was initially made in 1962, by chemist Dora Richardson.[17][18] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[19] Tamoxifen is available as a generic medication.[14] In 2020, it was the 317th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 900 thousand prescriptions.[20][21]
- ^ "NCI Drug Dictionary". 2 February 2011. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 12 September 2021.
- ^ "Tamoxifen Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 25 July 2019. Retrieved 27 January 2020.
- ^ "Tamoxifen citrate tablet, film coated". DailyMed. Retrieved 12 September 2021.
- ^ "Soltamox- tamoxifen citrate liquid". DailyMed. Retrieved 12 September 2021.
- ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
MorelloWurz2003was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
BrennerStevens2017was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
ChabnerLongo2011was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h Cite error: The named reference
Sanchez-SpitmanSwen2019was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
pmid23962908was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid21451508was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Nagar2010was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Nolvadex (Tamoxifen Citrate) tablets". DailyMed. 3 November 2016. Retrieved 12 September 2021.
- ^ a b "Tamoxifen Citrate". NCI. 26 August 2015. Archived from the original on 4 January 2016. Retrieved 28 November 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Tamoxifen Citrate". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 4 January 2014. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- ^ "Selective estrogen receptor modulators". Archived from the original on 9 December 2013. Retrieved 28 November 2015.
- ^ Cano A, Calaf i Alsina J, Duenas-Diez JL, eds. (2006). Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators a New Brand of Multitarget Drugs. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. p. 52. ISBN 9783540347422.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Viviane M 2017was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Jordan VC (January 2006). "Tamoxifen (ICI46,474) as a targeted therapy to treat and prevent breast cancer". British Journal of Pharmacology. 147 (Suppl 1): S269–S276. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706399. PMC 1760730. PMID 16402113.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- ^ "Tamoxifen Citrate - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 22 September 2020. Retrieved 7 October 2022.