
| |
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
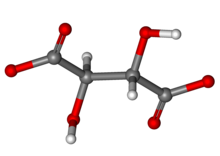
| C4H4O62− | |
| Molar mass | 148.07 g/mol |
| Conjugate acid | Bitartrate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
A tartrate is a salt or ester of the organic compound tartaric acid, a dicarboxylic acid. The formula of the tartrate dianion is O−OC-CH(OH)-CH(OH)-COO− or C4H4O62−.[1]
The main forms of tartrates used commercially are pure crystalline tartaric acid used as an acidulant in non-alcoholic drinks and foods, cream of tartar used in baking, and Rochelle salt, commonly used in electroplating solutions.
- ^ "Tartaric Acid - Compound Summary". PubChem.