 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Temodar, Temodal, Temcad, others[1] |
| Other names | TMZ |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601250 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | almost 100% |
| Protein binding | 15% (10–20%) |
| Metabolism | hydrolysis |
| Metabolites | 3-methyl-(triazen-1-yl)imidazole-4-carboxamide (MTIC, the active species); temozolomide acid |
| Elimination half-life | 1.8 hours |
| Excretion | mainly kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.158.652 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
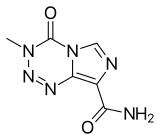
| Formula | C6H6N6O2 |
| Molar mass | 194.154 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 212 °C (414 °F) (decomp.) |
| |
| |
| | |
Temozolomide, sold under the brand name Temodar among others, is an anticancer medication used to treat brain tumors such as glioblastoma and anaplastic astrocytoma.[4][5] It is taken by mouth or via intravenous infusion.[4][5]
The most common side effects with temozolomide are nausea, vomiting, constipation, loss of appetite, alopecia (hair loss), headache, fatigue, convulsions (seizures), rash, neutropenia or lymphopenia (low white-blood-cell counts), and thrombocytopenia (low blood platelet counts).[5] People receiving the solution for infusion may also have injection-site reactions, such as pain, irritation, itching, warmth, swelling and redness, as well as bruising.[5]
Temozolomide is an alkylating agent used to treat serious brain cancers; most commonly as second-line treatments for astrocytoma and as the first-line treatment for glioblastoma.[4][6][7] Olaparib in combination with temozolomide demonstrated substantial clinical activity in relapsed small cell lung cancer.[8] It is available as a generic medication.
- ^ "Temozolomide". Drugs.com. 4 May 2020. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ "Temodal Capsules - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 24 October 2019. Archived from the original on 20 September 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ a b c d "Temodar- temozolomide capsule Temodar- temozolomide injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution". DailyMed. 31 January 2020. Archived from the original on 8 April 2021. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ a b c d e "Temodal EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 22 October 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ^ "Guidance on the use of temozolomide for the treatment of recurrent malignant glioma (brain cancer)" (PDF). 3 March 2016. Archived from the original on 11 July 2021. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ Sasmita AO, Wong YP, Ling AP (February 2018). "Biomarkers and therapeutic advances in glioblastoma multiforme". Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology. 14 (1): 40–51. doi:10.1111/ajco.12756. PMID 28840962.
- ^ Farago AF, Yeap BY, Stanzione M, Hung YP, Heist RS, Marcoux JP, et al. (October 2019). "Combination Olaparib and Temozolomide in Relapsed Small-Cell Lung Cancer". Cancer Discovery. 9 (10): 1372–1387. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0582. PMC 7319046. PMID 31416802.