This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2016) |
| Temple | |
|---|---|
 Location of temple | |
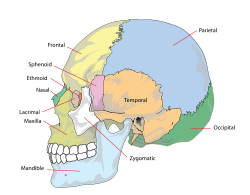 Human skull. Temporal bone is orange, and the temple overlies the temporal bone as well as overlying the sphenoid bone. | |
| Details | |
| Artery | Superficial temporal artery |
| Vein | Superficial temporal vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tempus |
| TA98 | A01.1.00.004 |
| TA2 | 103 |
| FMA | 46450 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The temple, also known as the pterion, is a latch where four skull bones intersect: the frontal, parietal, temporal, and sphenoid.[1] It is located on the side of the head behind the eye between the forehead and the ear. The temporal muscle covers this area and is used during mastication.
Cladistics classify land vertebrates based on the presence of an upper hole, a lower hole, both, or neither in the cover of dermal bone that formerly covered the temporalis muscle, whose origin is the temple and whose insertion is the jaw.
- ^ "8 Little Known Facts About the Temple". mentalfloss.com. 2017-11-01. Retrieved 2019-05-19.