 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | High |
| Elimination half-life | 30–140 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.149.365 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
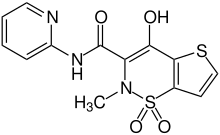
| Formula | C13H11N3O4S2 |
| Molar mass | 337.37 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 209 to 213 °C (408 to 415 °F) (dec.) |
| | |
Tenoxicam, sold under the brand name Mobiflex among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is used to relieve inflammation, swelling, stiffness, and pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis (a type of arthritis involving the spine), tendinitis (inflammation of a tendon), bursitis (inflammation of a bursa, a fluid-filled sac located around joints and near the bones), and periarthritis of the shoulders or hips (inflammation of tissues surrounding these joints).[1]
Tenoxicam belongs to the class of NSAIDs known as oxicams.
It was patented in 1974 by Roche and approved for medical use in 1987.[2] It is available as a prescription-only drug in the United Kingdom and other countries, but not in the US. Outside the United Kingdom, tenoxicam is also marketed under brand names including Tilatil, Tilcitin, and Alganex.[1][3]
- ^ a b "Medicines A-Z - Tenoxicam". NHS. Retrieved July 3, 2015.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 519. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ "Drugs.com international listings for Tenoxicam". Drugs.com. Retrieved July 3, 2015.