| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC names
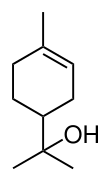
p-Menth-1-en-8-ol
2-(4-Methylcyclohex-3-en-1-yl)propan-2-ol | |||
| Other names
2-(4-Methyl-1-cyclohex-3-enyl)propan-2-ol
alpha-terpineol α-terpineol α,α,4-Trimethylcyclohex-3-ene-1-methanol Terpene alcohol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 2325137 | |||
| ChEBI |
| ||
| ChEMBL |
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
| ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
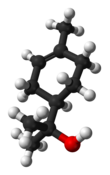
| C10H18O | |||
| Molar mass | 154.253 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] | ||
| Density | 0.93 g/cm3[1] | ||
| Melting point | −35.9 to −28.2 °C (−32.6 to −18.8 °F; 237.2 to 245.0 K)[1] (mixture of isomers) | ||
| Boiling point | 214–217 °C (417–423 °F; 487–490 K)[1] (mixture of isomers) | ||
| 2.42 g/L[1] | |||
| −111.9·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 88 °C (190 °F; 361 K)[1] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
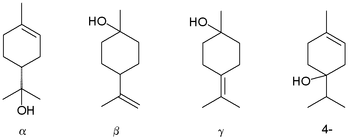
Terpineol is any of four isomeric monoterpenoids. Terpenoids are terpene that are modified by the addition of a functional group, in this case, an alcohol. Terpineols have been isolated from a variety of sources such as cardamom, cajuput oil, pine oil, and petitgrain oil.[2] Four isomers exist: α-, β-, γ-terpineol, and terpinen-4-ol. β- and γ-terpineol differ only by the location of the double bond. Terpineol is usually a mixture of these isomers with α-terpineol as the major constituent.
Terpineol has a pleasant odor similar to lilac and is a common ingredient in perfumes, cosmetics, and flavors. α-Terpineol is one of the two most abundant aroma constituents of lapsang souchong tea; the α-terpineol originates in the pine smoke used to dry the tea.[3] (+)-α-terpineol is a chemical constituent of skullcap.
- ^ a b c d e f Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 9103
- ^ Shan-Shan Yao; Wen-Fei Guo; Yi Lu; Yuan-Xun Jiang (2005). "Flavor Characteristics of Lapsang Souchong and Smoked Lapsang Souchong, a Special Chinese Black Tea with Pine Smoking Process". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 53 (22): 8688–93. doi:10.1021/jf058059i. PMID 16248572.