| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N,N-Triethylethanaminium | |
| Other names
Tetraethylazanium
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H20N+ | |
| Molar mass | 130.25 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
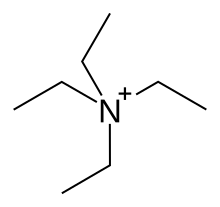
Tetraethylammonium (TEA) is a quaternary ammonium cation with the chemical formula [Et4N]+, consisting of four ethyl groups (−C2H5, denoted Et) attached to a central nitrogen atom. It is a counterion used in the research laboratory to prepare lipophilic salts of inorganic anions. It is used similarly to tetrabutylammonium, the difference being that its salts are less lipophilic, more easily crystallized and more toxic.