| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
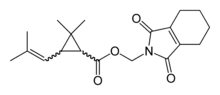
| IUPAC name
(1,3-Dioxo-4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoindol-2-yl)methyl 2,2-dimethyl-3-(2-methylprop-1-enyl)cyclopropane-1-carboxylate
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1,3-Dioxo-1,3,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-2H-isoindol-2-yl)methyl 2,2-dimethyl-3-(2-methylprop-1-en-1-yl)cyclopropane-1-carboxylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.829 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H25NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 331.406 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystalline solid |
| Odor | strong, pyrethrum-like |
| Density | 1.108 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 65 to 80 °C (149 to 176 °F; 338 to 353 K) |
| 0.00183 g/100 mL | |
| Solubility | soluble in methane, hexane slightly soluble in acetone, n-octanol, ethanol very slightly soluble in xylene |
| log P | 4.73 |
| Vapor pressure | 10 Pa |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.5175 |
| Pharmacology | |
| P03BA04 (WHO) QP53AC13 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
20,000 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tetramethrin is a potent synthetic insecticide in the pyrethroid family. It is a white crystalline solid with a melting point of 65–80 °C. The commercial product is a mixture of stereoisomers.
It is commonly used as an insecticide, and affects the insect's nervous system. It is found in many household insecticide products.[1]
Tetramethrin has an expected half-life of 12.5–14 days in soil and 13–25 days in water.[2] Tetramethrin was classified as a Category 2 carcinogen in 2018 by Directorate-General for the Environment of the European Commission.[3]
- ^ Tetramethrin in the Consumer Product Information Database
- ^ "Re-evaluation Decision RVD2018-01, Tetramethrin and Its Associated End-use Products". 23 February 2018.
- ^ "Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/1480 of 4 October 2018 amending, for the purposes of its adaptation to technical and scientific progress, Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures and correcting Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/776 (Text with EEA relevance.)". 4 October 2018.