 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | xantheose diurobromine 3,7-dimethylxanthine 3,7-dihydro-3,7-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
| Dependence liability | None |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic demethylation and oxidation |
| Elimination half-life | 6–8 hours[1][2] |
| Excretion | Renal (10% unchanged, rest as metabolites) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.359 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
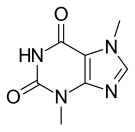
| Formula | C7H8N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 180.167 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.359 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.524 g/cm3[3] |
| Melting point | 351 °C (664 °F; 624 K) |
| 330 mg/L) | |
Theobromine, also known as xantheose, is the principal alkaloid of Theobroma cacao (cacao plant).[4] Theobromine is slightly water-soluble (330 mg/L) with a bitter taste.[5] In industry, theobromine is used as an additive and precursor to some cosmetics.[4] It is found in chocolate, as well as in a number of other foods, including tea (Camellia sinensis), some American hollies (yaupon and guayusa) and the kola nut. It is a white or colourless solid, but commercial samples can appear yellowish.[5]
- ^ Drouillard DD, Vesell ES, Dvorchik BH (March 1978). "Studies on theobromine disposition in normal subjects. Alterations induced by dietary abstention from or exposure to methylxanthines". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 23 (3): 296–302. doi:10.1002/cpt1978233296. PMID 627135. S2CID 10519385.
- ^ Lelo A, Birkett DJ, Robson RA, Miners JO (August 1986). "Comparative pharmacokinetics of caffeine and its primary demethylated metabolites paraxanthine, theobromine and theophylline in man". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 22 (2): 177–182. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb05246.x. PMC 1401099. PMID 3756065.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Actawas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b "Theobromine". PubChem, US National Library of Medicine. 27 August 2022. Retrieved 3 September 2022.
- ^ a b Smit HJ (2011). "Theobromine and the Pharmacology of Cocoa". Methylxanthines. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Vol. 200. pp. 201–234. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-13443-2_7. ISBN 978-3-642-13442-5. PMID 20859797.