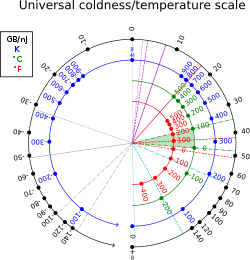
In statistical thermodynamics, thermodynamic beta, also known as coldness,[1] is the reciprocal of the thermodynamic temperature of a system: (where T is the temperature and kB is Boltzmann constant).[2]
Thermodynamic beta has units reciprocal to that of energy (in SI units, reciprocal joules, ). In non-thermal units, it can also be measured in byte per joule, or more conveniently, gigabyte per nanojoule;[3] 1 K−1 is equivalent to about 13,062 gigabytes per nanojoule; at room temperature: T = 300K, β ≈ 44 GB/nJ ≈ 39 eV−1 ≈ 2.4×1020 J−1. The conversion factor is 1 GB/nJ = J−1.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
1969Daywas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Meixner, J. (1975-09-01). "Coldness and temperature". Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis. 57 (3): 281–290. doi:10.1007/BF00280159. ISSN 1432-0673.
- ^ Fraundorf, P. (2003-11-01). "Heat capacity in bits". American Journal of Physics. 71 (11): 1142–1151. doi:10.1119/1.1593658. ISSN 0002-9505.

![{\displaystyle [\beta ]={\textrm {J}}^{-1}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/95d75d6e2e60e9f106f17e91bd18a413a3a9d6e9)
