 | |
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
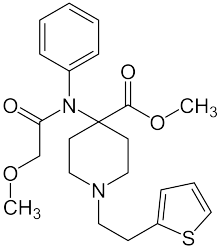
| Formula | C22H28N2O4S |
| Molar mass | 416.54 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Thiafentanil (A-3080, Thianil) is a highly potent opioid analgesic that is an analog of fentanyl, and was invented in 1986.[1] Its analgesic potency is slightly less than that of carfentanil (itself approximately 10,000 times the potency of morphine, or 4,000 times that of heroin),[2] though with a faster onset of effects, shorter duration of action and a slightly lesser tendency to produce respiratory depression. It is used in veterinary medicine to anesthetise animals such as impala, usually in combination with other anesthetics such as ketamine, xylazine or medetomidine to reduce the prevalence of side effects such as muscle rigidity.[3]
- ^ US expired US4584303A, Bao-Shan Huang, Ross C. Terrell, Kirsten H. Deutsche, Linas V. Kudzma, Nhora L. Lalinde, "N-aryl-N-(4-piperidinyl)amides and pharmaceutical compositions and method employing such compounds", published 22 April 1986, issued 22 April 1986, assigned to Boc, Inc. and Anaquest, Inc.
- ^ Leen JL, Juurlink DN (April 2019). "Carfentanil: a narrative review of its pharmacology and public health concerns". Can J Anaesth. 66 (4): 414–421. doi:10.1007/s12630-019-01294-y. PMID 30666589. S2CID 58642995.
- ^ Zeiler GE, Meyer LC (September 2017). "Chemical capture of impala (Aepyceros melampus): A review of factors contributing to morbidity and mortality". Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia. 44 (5): 991–1006. doi:10.1016/j.vaa.2017.04.005. PMID 29050999.