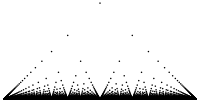
Thomae's function is a real-valued function of a real variable that can be defined as:[1]: 531
It is named after Carl Johannes Thomae, but has many other names: the popcorn function, the raindrop function, the countable cloud function, the modified Dirichlet function, the ruler function (not to be confused with the integer ruler function),[2] the Riemann function, or the Stars over Babylon (John Horton Conway's name).[3] Thomae mentioned it as an example for an integrable function with infinitely many discontinuities in an early textbook on Riemann's notion of integration.[4]
Since every rational number has a unique representation with coprime (also termed relatively prime) and , the function is well-defined. Note that is the only number in that is coprime to
It is a modification of the Dirichlet function, which is 1 at rational numbers and 0 elsewhere.
- ^ Beanland, Kevin; Roberts, James W.; Stevenson, Craig (2009), "Modifications of Thomae's Function and Differentiability", The American Mathematical Monthly, 116 (6): 531–535, doi:10.4169/193009709x470425, JSTOR 40391145
- ^ Dunham, William (2008), The Calculus Gallery: Masterpieces from Newton to Lebesgue (Paperback ed.), Princeton: Princeton University Press, page 149, chapter 10, ISBN 978-0-691-13626-4,
...the so-called ruler function, a simple but provocative example that appeared in a work of Johannes Karl Thomae ... The graph suggests the vertical markings on a ruler—hence the name.
- ^ John Conway. "Topic: Provenance of a function". The Math Forum. Archived from the original on 13 June 2018.
- ^ Thomae, J. (1875), Einleitung in die Theorie der bestimmten Integrale (in German), Halle a/S: Verlag von Louis Nebert, p. 14, §20





