| Thoracic aorta | |
|---|---|
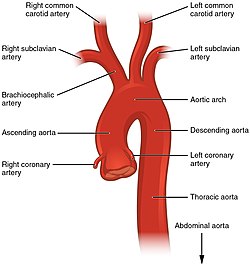 Schematic view of the aorta, showing major branches and segments with thoracic aorta shown as continuation of descending aorta | |
 The thoracic aorta, viewed from the left side. | |
| Details | |
| Source | Descending aorta |
| Branches | Bronchial arteries, esophageal arteries, posterior intercostal arteries, abdominal aorta, superior phrenic artery, pericardial arteries |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | aorta thoracalis |
| MeSH | D001013 |
| TA98 | A12.2.11.001 |
| TA2 | 4186 |
| FMA | 3786 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The thoracic aorta is a part of the aorta located in the thorax. It is a continuation of the aortic arch. It is located within the posterior mediastinal cavity, but frequently bulges into the left pleural cavity. The descending thoracic aorta begins at the lower border of the fourth thoracic vertebra and ends in front of the lower border of the twelfth thoracic vertebra, at the aortic hiatus in the diaphragm where it becomes the abdominal aorta.
At its commencement, it is situated on the left of the vertebral column; it approaches the median line as it descends; and, at its termination, lies directly in front of the column.
The thoracic aorta has a curved shape that faces forward, and has small branches. It has a radius of approximately 1.16 cm.[1]